Explanations of the China beef quota rules 2026-2028
 As of January 1, 2026, China has implemented new "safeguard" measures on beef imports to protect its domestic cattle industry. These rules introduce a strict Tariff Rate Quota (TRQ) system that will remain in effect for three years, through December 31, 2028.
As of January 1, 2026, China has implemented new "safeguard" measures on beef imports to protect its domestic cattle industry. These rules introduce a strict Tariff Rate Quota (TRQ) system that will remain in effect for three years, through December 31, 2028.
China beef imports
China’s beef imports have undergone significant shifts in recent years, peaking at record volumes in 2024 before the introduction of the 2026 safeguard quotas.
Import Trends (2023–2025)
2024 Record High: China imported a record 2.87 million metric tons of beef in 2024. This surge was driven by low-cost South American supplies and a recovery in consumer demand for premium proteins.
2025 Deceleration: For the first half of 2025, imports fell by 9.5% year-on-year to 1.3 million metric tons. Total imports for the first 11 months of 2025 reached approximately 2.6 million metric tons.
Price Collapse: A "flood" of cheap imports caused domestic wholesale beef prices to drop over 22% between 2023 and late 2024, falling to their lowest levels in five years (approx. 59.82 yuan/kg).
China beef imports Market Share
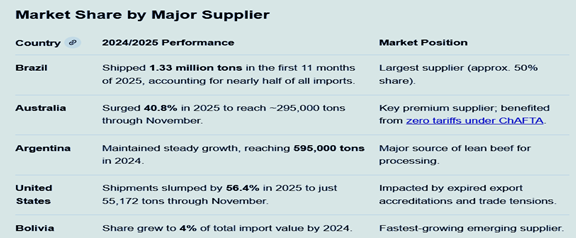
Recent Policy Drivers
Domestic situation: In late 2024, the China Animal Husbandry Association reported that most domestic cattle farms were operating at a loss, leading to the December 2024 safeguard investigation that resulted in the 2026 quotas.
Traceability Mandate: By the end of 2025, China expects a nationwide traceability system to be fully operational, requiring all imported beef to be tracked from farm to table.
Key Quota Rules for 2026-2028
Primary Quota Limit: The total global import quota for 2026 is set at 2.7 million metric tons.
High Over-Quota Tariffs: While shipments within the quota continue at current tariff rates (typically around 12%), any volume exceeding the set limit faces a steep 55% additional tariff.
Immediate Implementation: The quota counts actual entries into China starting January 1, 2026, regardless of when contracts were signed or if the cargo was already in transit.
Annual Escalation: The total quota is scheduled to increase slightly each year: 2.742 million tons in 2027 and 2.797 million tons in 2028.
2026 Country-Specific Quotas
Major beef exporters have been assigned specific annual limits based on historical market shares:
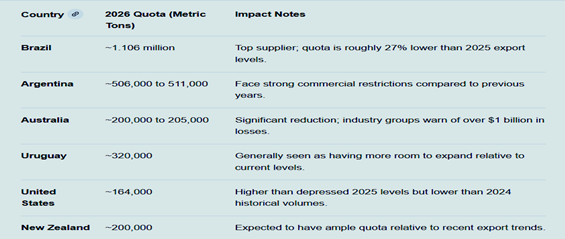
Operational Impact
No Rollover: Unused quota at the end of the year cannot be carried over to 2027.
Three-Day Grace Period: Once a country's annual quota is reached, the 55% tariff is applied to all shipments arriving from the third day onward.
Free Trade Agreement (FTA) Suspension: For countries like
Australia, China has paused certain compliance measures of existing FTAs (such as ChAFTA) to enforce these safeguard tariffs.
China beef quota rules 2026 – 2028
As stated above, China has implemented new safeguard measures on beef imports to protect its domestic cattle industry. These rules, effective from January 1, 2026, through December 31, 2028, impose strict annual quotas and high tariffs on excess volumes.
What are Quota & Tariff Rules for 2026 2028?
Total Import Quota: The aggregate limit for 2026 is set at approximately 2.7 million metric tons. This total is planned to increase incrementally each year, reaching 2.8 million tons by 2028.
Over-Quota Tariff: Any beef imported beyond a country’s specific allocation is subject to a steep 55% additional tariff. For the U.S., some industry reports suggest the total duty rate could jump to 77% when combining existing duties with the new surcharge.
Counting Shipments: China counts all entries toward the 2026 quota starting January 1, including cargo already in transit or held at ports awaiting clearance from 2025.
Country-Specific 2026 Allocations
China has assigned fixed quota shares to its primary beef suppliers:
Exporting Country | 2026 Quota Allocation (Metric Tons) |
Brazil | 1,106,000 |
Argentina | 506,000 to 511,000 |
Uruguay | 324,000 |
Australia | 200,000 to 205,000 |
United States | 164,000 |
How about Compliance?
Suspension of ChAFTA: For Australian exporters, China has paused certain compliance measures under the China-Australia Free Trade Agreement (ChAFTA) to enforce these new safeguards.
Facility Registration: Beyond quotas, U.S. exporters face additional hurdles; as of early 2026, many U.S. facilities must re-register after their eligibility expired in 2025.
Negotiation Factors: Argentina is reportedly seeking a bilateral reinterpretation of the rules to exclude certain "bone-in" products from the quota count to gain a competitive edge.











